|
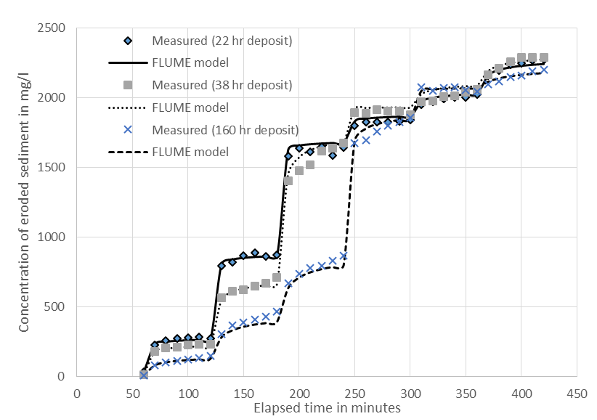
Krishnappan BG, Stone M, Granger SJ, Upadhayay HR, Tang Q, Zhang Y, Collins AL. Experimental Investigation of Erosion Characteristics of Fine-Grained Cohesive Sediments. Water 2020, 12(5): 1511. Brief summary Cohesive sediment plays an important role in the transport and fate of pollutants and is a key driver of water quality degradation in aquatic systems such as rivers and reservoirs. Knowledge of cohesive sediment transport processes (erosion, deposition and flocculation) is critical for the development of reliable numerical models designed to simulate cohesive sediment and associated contaminant transport dynamics. In this study, the erosion behavior of cohesive sediment collected from the upper River Taw in South West England was studied in a rotating annular flume located in the National Water Research Institute in Burlington, Ontario, Canada in order to model the transport of fine sediment and the associated nutrients in the River Taw. The results show that eroded sediment is transported in a flocculated form due to the presence of microorganisms and organic matter. The experimental data and the fitting coefficients were established as a function of bed shear stress and depositional history of sediment and applied to a fine sediment transport model (FLUME) which accurately simulated the erosion experiments in a rotating circular flume deposit. Key messages
Research Photos
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
forWater NetworkThe Network provides insights into new scientific research for safe, secure drinking water---globally---which starts with resilient forests Archives
October 2023
Categories |








 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

